4 useful ways to manage psoriatic arthritis
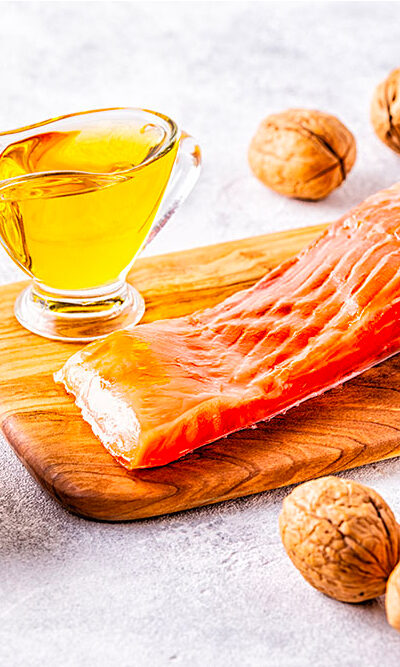
Psoriatic arthritis (PsA) is a health condition that affects about 30% of people affected by psoriasis, bringing the number of patients in the country to around 2 million. Just like psoriasis causes inflammation of the skin, Psoriatic arthritis results in inflammation of the joints. The best way to manage this condition is a combination of medical treatment and lifestyle changes. Here are some essential management tips necessary to manage psoriatic arthritis and reduce flare-ups: Treatment options Doctors might have to go through various treatment plans since finding one that suits the patient isn’t easy. That said, there are some options that show substantial results and are commonly prescribed. These include the following. OTEZLA® Approved by the FDA, OTEZLA® is a prescription treatment option for patients with psoriatic arthritis. It acts by inhibiting the phosphodiesterase 4 (PDE4) enzyme that is the cause of the increased inflammatory response of the body. Regular use of OTEZLA® has proven beneficial for patients and can be combined with phototherapy or topical treatments. RINVOQ® RINVOQ® is an oral treatment option for active psoriatic arthritis patients. Doctors usually prescribe this treatment option when patients fail to respond to one or more tumor necrosis factor (TNF) blockers. It is an oral treatment option used for adult PsA patients only. Foods to eat and avoid Omega 3 helps lower inflammation in the body and improves bone health. Some foods that need to be included in regular meals are salmon, walnuts, and seeds. Fruits and vegetable portions also need to be increased as they provide the body with necessary nutrients and have anti-inflammatory properties. Similarly, foods with inflammatory properties can contribute to the worsening of symptoms in patients with PsA. These include foods like dairy and dairy products, sugar, processed meat, red meat, fried foods, and processed food products. Lowering the intake of these food groups can show improvement in the patient’s condition.