Repigmentation – Its role in managing vitiligo
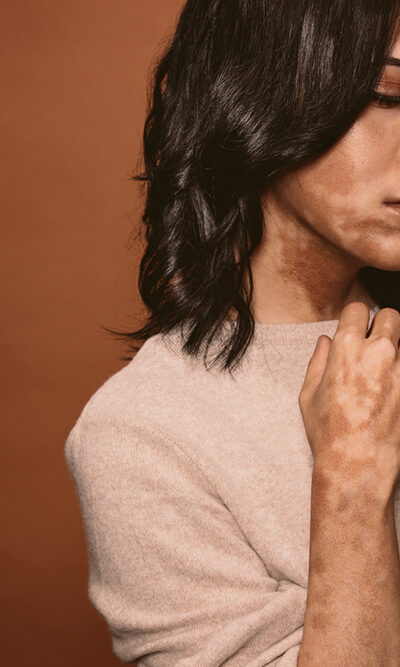
The skin gets its pigment or natural color from melanin-producing cells known as melanocytes, which also protect the skin from the sun’s harmful effects. Certain conditions, like vitiligo, often classified into segmental and nonsegmental, can cause abnormal melanocyte development. Depending on the type, the skin can gradually or rapidly start losing its color in certain or all areas of the body. So, individuals with vitiligo may require treatment involving repigmentation or restoring the skin’s pigment. Nonsegmental vitiligo vs segmental vitiligo In nonsegmental or bilateral vitiligo, the skin on both sides of the body starts to lose its natural pigmentation. For instance, the condition might cause symmetrical white patches to appear on either side of the body, such as on both hands or knees. It is an autoimmune disorder and is often triggered by other autoimmune conditions like Hashimoto’s thyroiditis and Addison’s disease. This form differs from segmental vitiligo, which causes rapid pigment loss on just one side. After 6 to 12 months, this type of vitiligo stops spreading. This means the color loss stops, and no new patches or spots develop. Repigmentation to manage vitiligo Repigmentation involves restoring the color or natural pigment of the skin with the help of various processes, such as light therapy or surgery. Often, repigmentation is one of the main ways of managing the condition and is usually done if an individual has widespread vitiligo. Light therapy Also known as phototherapy, light therapy involves using light boxes, medical-grade lasers, or UVB or ultraviolet light sources. Here, the skin is exposed to any of these sources over several sessions to restore its pigment. Surgery This can involve procedures like skin grafting and blister grafting. Skin grafting involves using skin from one part of the body to cover a vitiligo-affected part. A similar procedure is followed with blister grafting.